|
Compounds of sulfur
Sulfates: SO42- = ion sulfate. Examples:
Sodium sulfate (Glauber's salt): Na2SO4.
 Peroxydisulfuric acid: H2S2O8, is an
extremely powerful oxidizing agent. The oxidation reaction is slow but
can be catalyzed by silver ions.
Peroxydisulfuric acid: H2S2O8, is an
extremely powerful oxidizing agent. The oxidation reaction is slow but
can be catalyzed by silver ions.
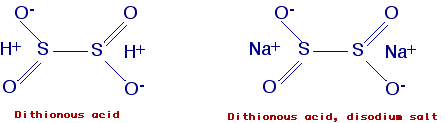
Dithionous acid, disodium salt (synomims:
Sodium dithionite; sodium hydrosulfite, Sodium sulfoxylate; Virtex L;
Reductone; Hydrolin; Vatrolite )
Sulfurous acid (H2SO3) is the hydrated
form of sulfur dioxide (SO2), a colorless gas
with a characteristic choking odor. It is a weak acid which can dissociate
into bisulfite (HSO3-) and sulfite
(SO32-) ions.
|
H2O (l) + SO2(g) = H2SO3
= HSO3- + H+
|
HSO3- = SO32- + H+
|
In acidic solution, the equilibria are shifted to form sulfurous acid,
resulting in the evolution of SO2 gas. Sulfite ion is readily
oxidized to sulfate, e.g. by prolonged exposure to atmospheric oxygen
or by permanganate. The decolorization of permanganate solutions serves
as a convenient test for sulfur dioxide. The sulfites of Na+,
K+, and NH4+ are soluble in water. Most
other sulfites are insoluble in water. However, due to the basic nature
of SO32-, all sulfites dissolve in acidic solution.
|
 Peroxydisulfuric acid: H2S2O8, is an
extremely powerful oxidizing agent. The oxidation reaction is slow but
can be catalyzed by silver ions.
Peroxydisulfuric acid: H2S2O8, is an
extremely powerful oxidizing agent. The oxidation reaction is slow but
can be catalyzed by silver ions.
