| I work withProf. Lucio Sansone, Prof. Antonio Picariello, Prof. Angelo Chianese, Prof. Antonino Mazzeo and Doct. Vincenzo Moscato of the University of Naples Federico II and Prof. VS Subrahmanian and Doct. Diego Reforgiato Recupero of the University of Maryland at College Park.
OASYS
 There are numerous applications in which we would like to assess what opinions are being expressed in text documents. For example, Martha Stewart's company may have wished to assess the degree of criticism of a proposed dam in Bangladesh. The ability to gauge opinion on a given topic is therefore of critical interest. In this project, we developed a suite of algorithms which takes as input, a set D of documents as well as a topic t, and gauge the degree of opinion expressed about topic t in the set D of documents. Our algorithms can return both a number (larger the number, more positive the opinion and lower the number, more negative the opinion) as well as a qualitative opinion. We assessed the accuracy of these algorithms via human experiments and showed that the best of these algorithms can accurately reflect human opinions. We developed Oasys, (Opinion Analysis SYStem) ( http://oasys.umiacs.umd.edu/oasys ); it is a system which crawls documents from the web finding new interesting topics and, by using our opinion analysis algorithms, it gives opinions on them. There are numerous applications in which we would like to assess what opinions are being expressed in text documents. For example, Martha Stewart's company may have wished to assess the degree of criticism of a proposed dam in Bangladesh. The ability to gauge opinion on a given topic is therefore of critical interest. In this project, we developed a suite of algorithms which takes as input, a set D of documents as well as a topic t, and gauge the degree of opinion expressed about topic t in the set D of documents. Our algorithms can return both a number (larger the number, more positive the opinion and lower the number, more negative the opinion) as well as a qualitative opinion. We assessed the accuracy of these algorithms via human experiments and showed that the best of these algorithms can accurately reflect human opinions. We developed Oasys, (Opinion Analysis SYStem) ( http://oasys.umiacs.umd.edu/oasys ); it is a system which crawls documents from the web finding new interesting topics and, by using our opinion analysis algorithms, it gives opinions on them.
Story
 There are thousands of applications where we wish to derive a story about a particular event or a person or phenomenon. For example, consider an application where a person is walking through an archaeological site such as Pompeii. Though a casual tourist may be satisfied with the simple title which usually marks exhibits, a person with a deeper interest may be unsatisfied. In the same vein, consider a US military soldier stationed at a checkpoint in Baghdad - he or she may want to know a person's "story" in order to make critical security decisions. As the diversity of the two previous applications shows, what goes into a story depends not only on the basic facts, but also on the specific items of interest to the listener. We formally define a story to be a set of facts about a given subject that satisfies a "story length" constraint. An optimal story is a story that maximizes the value of an objective function measuring the goodness of a story. There are thousands of applications where we wish to derive a story about a particular event or a person or phenomenon. For example, consider an application where a person is walking through an archaeological site such as Pompeii. Though a casual tourist may be satisfied with the simple title which usually marks exhibits, a person with a deeper interest may be unsatisfied. In the same vein, consider a US military soldier stationed at a checkpoint in Baghdad - he or she may want to know a person's "story" in order to make critical security decisions. As the diversity of the two previous applications shows, what goes into a story depends not only on the basic facts, but also on the specific items of interest to the listener. We formally define a story to be a set of facts about a given subject that satisfies a "story length" constraint. An optimal story is a story that maximizes the value of an objective function measuring the goodness of a story.
Topic Detection and Tracking System 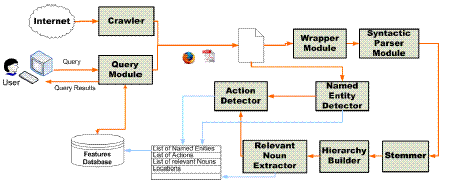 The Web is nowadays the biggest and most various existing knowledge base, providing users with huge amount of data in disparate fields. The data spread out on the Net, the newspapers, the on-line magazine and in general the web are, in fact, of strategic importance to a plethora of applications, such as business, defense agencies, etc.. The Web is nowadays the biggest and most various existing knowledge base, providing users with huge amount of data in disparate fields. The data spread out on the Net, the newspapers, the on-line magazine and in general the web are, in fact, of strategic importance to a plethora of applications, such as business, defense agencies, etc..
On the other hand, the size and disorganization of these data poses great problems for what concerns access to and retrieval of relevant documents, greatly complicating the task of browsing the information retrieved by search engines. In latest years many efforts have been made to develop systems apt to simplify the browsing through retrieved documents. Most recent approaches mainly rely on exploiting the semantics of keywords provided by the user as input query, with or without the help of external knowledge bases (e.g., Wordnet or some specialized ontology) or user feedback. Other approaches instead rely on the identification and modeling of topics in retrieved documents and the design of opportune clusters, devoting most efforts towards a better organization of the information. We believe that both this aspects are to be considered very relevant to the aim of an effective document retrieval, so we have addressed both them and developed a retrieval system that semantically parses documents (retrieved from the Web by means of a crawling agent and stored in a local news database) and clusters them on the basis of the characterizing topics. The input query can either consist of a few keywords, as in traditional systems, or of an example document, based on which the system can infer the topics of interest, with an approach similar to the one followed by modern Topic Detection systems
Orpheus
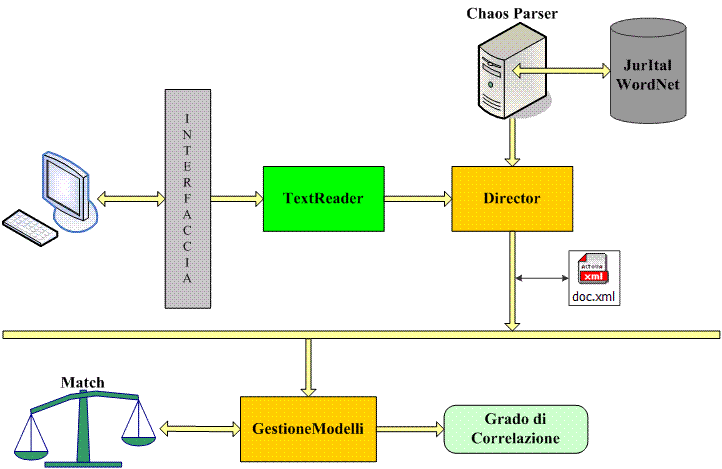 It is a system that allows to perform semantic search, document comparison and feature extraction from legal documents. It is a system that allows to perform semantic search, document comparison and feature extraction from legal documents.
The core of the system relies on the ability to extract
a suitable set of features used to relize a legal reasoning of the document considering also the dialectic dimension of law (deontic modalities,
defeasible reasoning, argument construction).
An ontology-based approach offers a solid support in the process
 http://www.grid.unina.it/projects/firb/ http://www.grid.unina.it/projects/firb/
|




 There are numerous applications in which we would like to assess what opinions are being expressed in text documents. For example, Martha Stewart's company may have wished to assess the degree of criticism of a proposed dam in Bangladesh. The ability to gauge opinion on a given topic is therefore of critical interest. In this project, we developed a suite of algorithms which takes as input, a set D of documents as well as a topic t, and gauge the degree of opinion expressed about topic t in the set D of documents. Our algorithms can return both a number (larger the number, more positive the opinion and lower the number, more negative the opinion) as well as a qualitative opinion. We assessed the accuracy of these algorithms via human experiments and showed that the best of these algorithms can accurately reflect human opinions. We developed Oasys, (Opinion Analysis SYStem) (
There are numerous applications in which we would like to assess what opinions are being expressed in text documents. For example, Martha Stewart's company may have wished to assess the degree of criticism of a proposed dam in Bangladesh. The ability to gauge opinion on a given topic is therefore of critical interest. In this project, we developed a suite of algorithms which takes as input, a set D of documents as well as a topic t, and gauge the degree of opinion expressed about topic t in the set D of documents. Our algorithms can return both a number (larger the number, more positive the opinion and lower the number, more negative the opinion) as well as a qualitative opinion. We assessed the accuracy of these algorithms via human experiments and showed that the best of these algorithms can accurately reflect human opinions. We developed Oasys, (Opinion Analysis SYStem) ( 